Search:
Revision states with critical risk-matrix rank
Explanation:
A search will be made for revision states whose rank (according to the Risk Matrix) exceeds a predefined limit. The default limit is set to 9, but this can be changed by the user. Since there are 27 colour triplets in total, the limit must be between 1 and 27. 1 is the best (all green) and 27 the worst (all red).
Example:
Abbreviations
- ASIL = Automotive safety integrity level
- BF = Base failure of a base function
- BFn = Base function of a base structure element
- BSE = Base structure element
- Cl Prc = Classification for process characteristic
- Cl Prd = Classification for product characteristic
- Cl Req = Classification for requirement
- CM = Control method
- DA = Detection action
- DC = Diagnostic coverage
- DSCF = Dangerous safety critical failure
- Er Det = Error detection
- Er Resp = Error response
- F = Failure
- FIT = Failure in time
- Fn = Function
- FSM = Functional safety management
- IE = Inspection equipment
- LF = Latent fault
- LFM = Latent fault metric
- OC = Operating condition
- PA = Preventive action
- PE = Process element
- PFH = Probability of failure per Hour
- PMHF = Probabilistic metric for random hardware failures
- PrcC = Process characteristic
- PrdC = Product characteristic
- QM = Quality method
- QR = Quality rule
- Req = Requirement
- RMR = Risk Matrix Ranking
- RP = Reaction plan
- SE = Structure element
- SE ErDet = Structure element for error detections
- SE ErResp = Structure element for error responses
- SFF = Safe failure fraction
- SG = Safety Goal
- SIL = Safety integrity level
- SM = Organisational-SE for “safety mechanisms”
- SPF = Single point fault
- SPFM = Single point fault metric
- TF = Top failure of a top function
- TFn = Top function at root element
- TS = Test sample
Risk matrix set:
A risk matrix set consists of three risk matrices that are generated by the combination SxO, SxD and DxO valuations. Each matrix can be configured by the IQ user in the Data Manager (Administration / Risk matrices). Here you can determine the assignment of green, yellow and red combinations.
The following image shows how the risk matrix set is as standard within the IQ-Software.
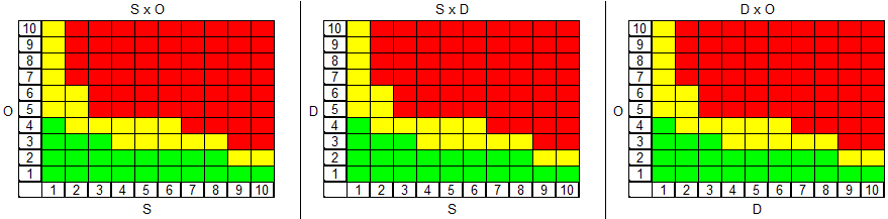
For every action/revision state, if the ratings S, O & D are determined, the corresponding valuation is displayed in one of the three colours. The red area is considered the most critical.
RMR table:
The RMR table aims to bundle the individual risks contained in the three risk matrices SxO, SxD and DxO for any given action state and to output the overall risk “in one value” as RMR.
The RMR is determined from the colour combinations of the three risk matrices of the risk matrix set. Since each risk matrix has three colors, a total of 27 different green-yellow-red color combinations can be formed, of which the color combination green-green-green represents the lowest (RMR = 1) and the color combination red-red-red the highest overall risk potential (RMR = 27). As an FMEA operator, you can decide for yourself where you want to place the other colour- and thus risk combinations.
The following image shows the standard setting for the IQ-Software.
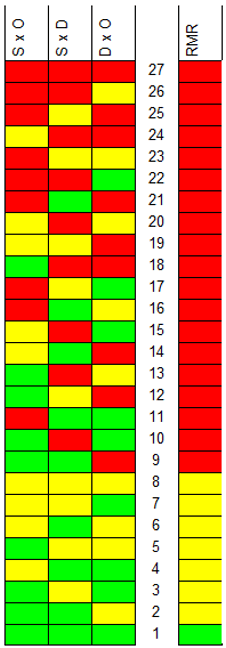
For the purpose of increased clarity, the 27 risk matrix ranks can also be marked with the colours green, yellow and red and thus assigned to three risk groups. In the case shown, all RMRs that have the colour red at least once in the colour triad are themselves shown as red and thus critical. As an IQ user, you as well have the possibility to change the colour assignment to the risk matrix ranks. For logical reasons, however, you should adhere to the rule that above a yellow RMR no green marking may occur and above a red marking any other colour is prohibited.
If you ignore this rule, this Quality Rule will not filter correctly, as the search will find all action states with risk matrix ranks which are higher or equal to the first one marked in red.
Example description:
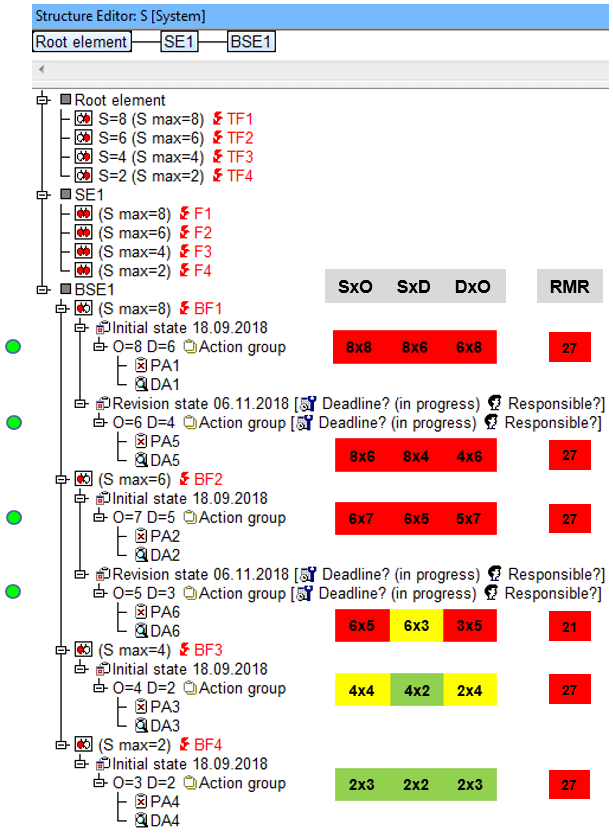
- The example structure shown consists of three structure elements, each of which has four failures. While the severity of failure is always found at the top failure, the preventive and detection actions are assigned to the base failures. Finally, the (O)ccurence and (D)etection ratings are anchored in their corresponding action groups.
- This Quality Rule aims to detect those action/revision states that have a critical RMR. Critical risk matrix ranks are those that are marked in red.
- There is currently no display option (September 2019) within the IQ-Software to show the variations or SxO, SxD and DxO in the Structure Editor. As such, the image above has these ratings with the RMR included pasted by hand.
- By using the FMEA Form Editor, it is possible to see these ratings in their own columns (note: see display options if they are not visible). The following image is the same example using the FMEA Form Editor.
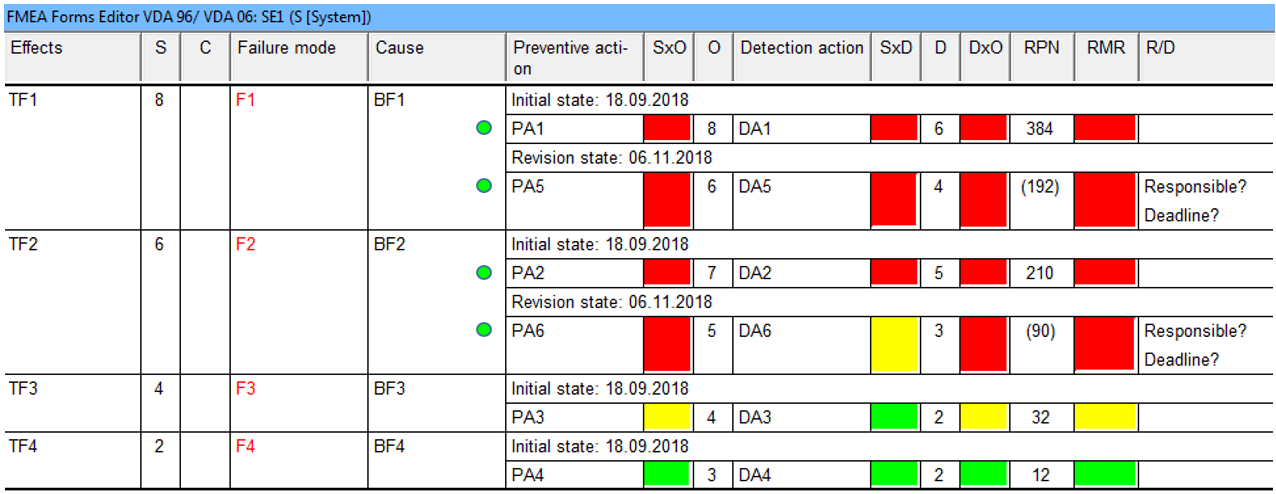
- Using the images of both the Structure Editor and the FMEA Form, it is possible to see which action states have a critical RMR.
- Analysiert man nun im Hinblick auf die hier beschriebene Qualitätsregel sowohl das Bild des Struktur-Editors als auch das Bild des Formblatt-Editors, zeigt sich, dass es vier Maßnahmenstände mit einem kritischen RMR gibt. Diese Risikomatrixränge sind alle rot markiert, weshalb man folgendes Suchergebnis erhält:
Search result: ![]()
This Quality Rule delivers four results whereby both Initial- and revision states anchored at BF1 & BF2 are hits.


